LFP vs NMC Battery, which is better? LFP batteries are about 20-30% cheaper per kWh, but system integration costs tend to be only about 5-15% cheaper at the beginning of the overall system life cycle.
What Is An LFP Battery?
LFP batteries also means LiFePO4 battery, which is a highly stable but slightly less energy dense battery composition. The iron and phosphate used to make the cathode are abundant and cheap than some of the materials used in NMC batteries – mainly cobalt. In addition, the materials in LFP batteries are far less toxic than those in NMC, making them easier to recycle at the end of their life.
Currently, more and more companies have been manufacturing LFP batteries as opposed to NMC for home energy storage. Mostly because LFP batteries are safer and more stable. In ELB, there are two model are popular in home energy storage system:
The big headlines this year in terms of LFP batteries have been about Tesla. Tesla announced in 2021 that they would be switching all Standard Range models to LFP battery chemistries.
LFP Summary Table
| Voltages | 3.20, 3.30V nominal; typical operating range 2.5–3.65V/cell |
| Specific energy (capacity) | 90–120Wh/kg |
| Charge (C-rate) | 1C typical, charges to 3.65V; 3h charge time typical |
| Discharge (C-rate) | 1C, 25C on some cells; 40A pulse (2s); 2.50V cut-off (lower that 2V causes damage) |
| Cycle life | 2000 and higher (related to depth of discharge, temperature) |
| Thermal runaway | 270°C (518°F) Very safe battery even if fully charged |
| Cost | ~$200 per kWh |
| Applications | ESS, EVs, etc |
What Is An NMC Battery?
An NMC battery also means NiCoMn ternary battery. Which is a very high specific energy or power battery. This limitation of “energy” or “power” makes them more commonly used in power tools or electric cars.
NMC batteries typically have a lower upfront cost but may need to be replaced over the lifetime of the vessel depending on the operational profile. NMC batteries have been the subject of a number of investigations around fires on both land-based and marine installations, leading some companies, such as Tesla, to completely switch over to the use of LFP chemistry for the EVs.
NMC Summary Table
| Voltages | 3.60V, 3.70V nominal; typical operating range 3.0–4.2V/cell, or higher |
| Specific energy (capacity) | 150–220Wh/kg |
| Charge (C-rate) | 0.7–1C, charges to 4.20V, some go to 4.30V; 3h charge typical. Charge current above 1C shortens battery life. |
| Discharge (C-rate) | 1C; 2C possible on some cells; 2.50V cut-off |
| Cycle life | 1000–2000 (related to depth of discharge, temperature) |
| Thermal runaway | 210°C (410°F) typical. High charge promotes thermal runaway |
| Cost | ~$420 per kWh |
| Applications | E-bikes, medical devices, EVs, industrial |
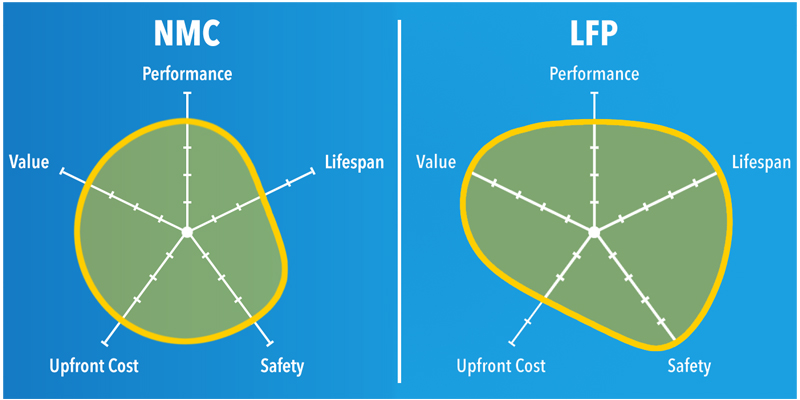
NMC vs LFP, What Is The Difference?
Performance
Overall, the overall performance of NMC and LFP cells is almost the same. You can find these two types in a variety of sizes, from as little as 0.5 kWh to over 100 kWh. Most homeowners only need about 10 kWh of storage, and you can definitely find it from both types.
That being said, there are some subtle differences between the two. Compared to NMCs, LFPs are slightly more efficient and operate better at lower states of charge, but NMCs can tolerate cooler temperatures better. However, if your battery is installed inside, or if you’re in an area that doesn’t experience significant temperature extremes, you probably don’t need to worry about this.
NMC batteries also have higher energy density, which means they will be physically smaller than LFP batteries of the same capacity. This is usually not a concern for homeowners, but if you have limited space then you may want to consider NMC batteries.
Lifespan
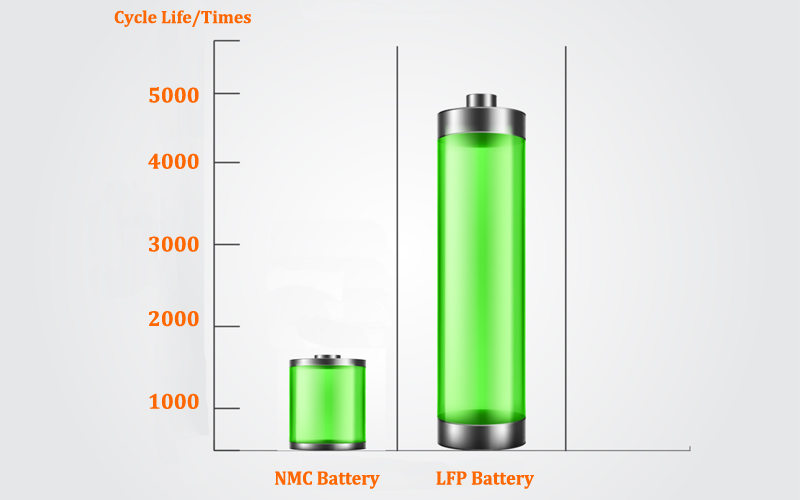
Generally speaking, the cycle life of lithium iron phosphate battery is more than 6000 times, while the life of ternary battery is generally 800-1000 times.
Safety
One of the biggest benefits of choosing an LFP battery is its safety and lifespan. The combination of lithium iron phosphate is more stable than nickel manganese cobalt at higher temperatures.
Additionally, LFP batteries can better handle greater power consumption. Therefore, LFP cells are less likely to experience thermal runaway. In short, LFP batteries are less likely to catch fire than NMC batteries.
This is not to say that if you install an NMC battery, it will spontaneously ignite. However, if the NMC battery is overstressed or mishandled, there is a higher chance of problems. That’s why it’s important to use a licensed, trusted battery installer to minimize the chance of problems.
Upfront Cost
NMC batteries tend to be a little more expensive than LFP batteries.
Also, the LFP battery is slightly larger, and the cabinet housing the LFP battery may also require more material.
Value
We’re just saying that NMC batteries have a lower upfront cost. However, LFP batteries can give you great value for money.
According to the price of each cycle life, the price per cycle of LFP Battery is only 1/3 of the price per cycle of NCM battery
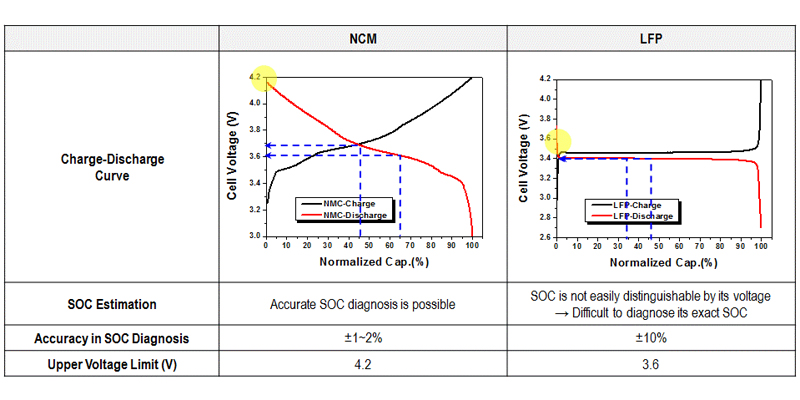
Charge-Discharge Curve
Let’s compare the charge-discharge curves of NCM and LFP batteries:
The state of charge (SOC) of an NCM battery varies significantly by its voltage level.
On the other hand, the SOC level of lithium iron phosphate batteries, due to its flat charge-discharge curve, is not easy to distinguish by voltage level.
Therefore, accurate SOC diagnosis of NCM batteries is possible, while SOC accuracy of LFP batteries is very challenging.
How To Choice The Right One For You?
Commercially, the initial capital expenditure for LFP cells is generally cheaper than for NMC cells. LFP batteries are about 20-30% cheaper per kWh, but system integration costs tend to be only about 5-15% cheaper at the beginning of the overall system life cycle.
Operationally, we like the LFP’s more relaxed operating conditions – a wider temperature range than NMC, and does not require refrigerated containers for shipping. In addition, LFP battery products generally support up to 1C operation, while NMC must use power batteries, 2H or 4H different batteries use batteries, support 1C rate (1 hour) applications, and the cost is high.
We believe it is important that customer and investor awareness of NMC’s products and companies remains high. But leading lithium iron phosphate batteries and companies have been catching up. Once a product is approved, customers can often easily adopt the same company’s new platform.





